Table of Contents
The “Helpful Content Update” is an algorithm update by Google that helps reward content that gives users a satisfying experience. The “Helpful Content Update” is a site-wide signal that can hurt the visibility of all content if too many articles are deemed “unhelpful”. It began rolling out on August 25, 2022 and finalized on September 9, 2022.
Related Content:
- SEO Agency
- B2B SEO Services
- SaaS SEO Agency
- Technical SEO Agency
- Ecommerce SEO Agencys
- Enterprise SEO Services
In order to help SEOs and websites better prepare for this update, we decided to create some guidelines that may help SEOs and site owners better navigate the Helpful Content Update. Please note that these are only predictions. As the update continues to roll out, there will be more information on what types of sites this impacts and which strategies work best.
1. Avoid Obviously Scaled Content Strategies
One of the biggest battles between Google and content creators is that of scaled content. For content creators it makes a ton of sense to think about ways to naturally scale the creation of your assets. More content means more indexable assets. This in turn can create more opportunities for organic traffic and ultimately conversions.
However, the idea of scaled content is a huge threat to Google’s product. Imagine if the top ranking results were all poorly written articles from a high authority domains that had been generated by some type of AI. The content might not help the user accomplish their goal but the authority of the site was able to help the page stand up tall in the search results. The result would be a poor user experience within Google search and over time there could be a risk of searchers migrating to other platforms.
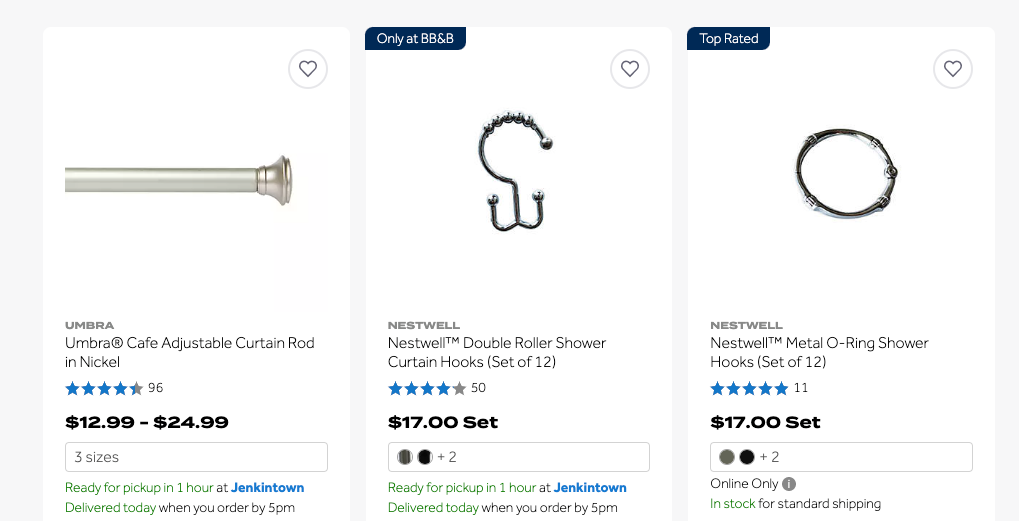
While most are looking at this within the context of informational articles written by AI, I think there are also other applications of scaled content that could be impacted by this update. In the eCommerce space, a strategy many strong domains have used is to allow their internal search pages to be indexed. Bed Bath and Beyond has generated millions of sessions and likely large numbers of sales from this strategy alone.
However, these pages are not always the most helpful for users.
Depending on product categorization, these search pages frequently return products that are not actually relevant to the core topic. For instance, the Bed Bath and Beyond page ranking for “shower curtain rods” has many shower hook products that wouldn’t be helpful to the end user.
With the announcement of this update, I believe Google is firing a warning shot to sites that have used scaled content strategies. While they’ve repeatedly stated that autogenerated content is against their guidelines, this algorithm update doubles down on that message.
I’d recommend staying away from scaling content strategies too much. If you’re using some type of AI-generated content I’d recommend using that as a first draft and have your experts review and rewrite the content to ensure that their perspective and insights are added. Those are the unique points that will go along way towards helping your content perform well.
2. Keep Your Content Aligned To Your Core Value Proposition
The growth that SEO has seen in the past decade has been phenomenal. If you’ve been around the industry that long, there’s no denying that SEO has been getting more adoption from senior marketers. This has resulted in the expansion of agencies, bigger in-house teams and more marketers choosing search as a viable career path.
During this time, companies have realized that they have been missing out on huge market share opportunities within their own industries. As a result, they’ve built out teams, created strategies and executed the creation of new content to fill those gaps. Generally speaking this has been a net positive for Google as more competitive content gives them more options to serve in search, improving the quality of their product.
However, a negative consequence of these investments has emerged. It’s no secret that bigger, more established sites generally have an easier time ranking. Somewhere along the line, companies have realized just how powerful of assets their sites are. This has resulted in companies not only filling gaps within their immediate industries but penetrating into new markets that they never belonged to in the first place.
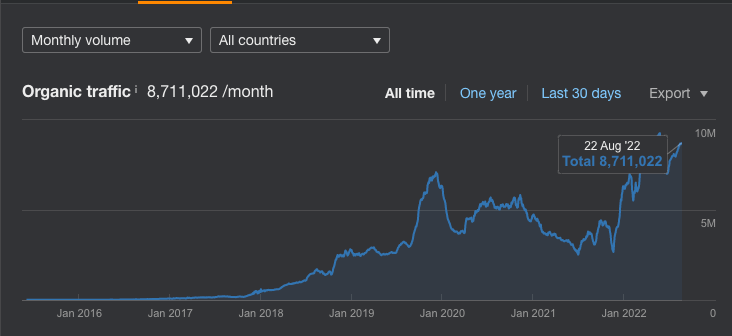
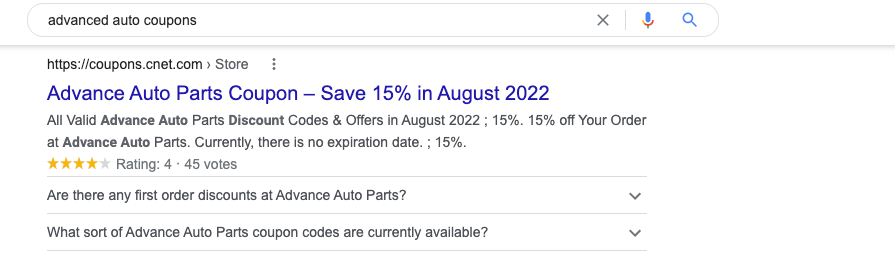
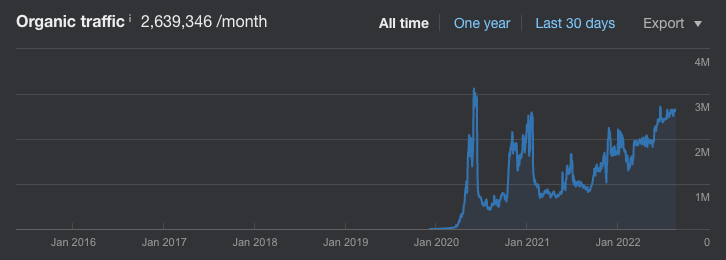
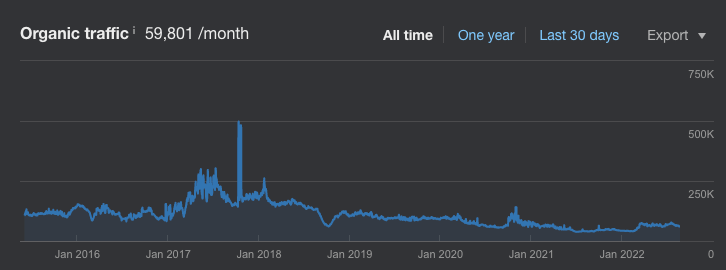
For instance, CNET is primarily a tech news site. However, they’ve created an entire subdomain (coupons.cnet.com) that’s dedicated solely to aggregating coupon deals. Currently, this site performs exceptionally well for many coupon terms such “advanced auto coupons”.
This foray into the coupon world has netted them an additional 2.6M organic sessions every month, in just the span of two years.
Here you can see the immense power of a strong domain at work. In a very short amount of time, they’ve been able to amass huge quantities of traffic despite not having a topically relevant site.
I believe that Google is trying to further move away from this power. This is even called out in one of their questions
“Did you decide to enter some niche topic area without any real expertise, but instead mainly because you thought you’d get search traffic“.
If websites are ranking on queries that aren’t directly relevant to their niche or core value proposition, they could be more at risk during this update.
During past updates, we’ve even seen Google take steps to reduce this kind of behavior. Entrepreneur.com is a magazine and website that has traditionally written about business and management. However, at some point they created a franchises section of their site that aggregates the top franchises across different industry categories. While one could make the argument that franchises are business-related, it’s a loose tie-in at best.
Slowly but surely we’ve seen this section gradually fall off in terms of organic traffic in favor of more relevant topical authorities.
Google’s new “Helpful Content Update” might be a continuation of the same trend. Rewarding the topically relevant sites and potentially harming sites that have branched into too many adjacent markets. If you have content outside of the core value proposition of your business, I’d recommend monitoring it very closely to see how it performs in the rankings over time.
3. Leverage The Concept Of Information Gain Scores
On of my favorite patents analyzed by the late Bill Slawski is the concept of information gain scores. In this article, Bill talks about how Google is looking for net new content in new articles added to the index:
“An information gain score for a given document indicates “additional information included by a page beyond the information contained in other pages already presented to the user.”
In this patent, Google talks about how they look for similar information within multiple documents and potentially reward documents that provide content that the user isn’t likely to have seen before.
Thus it stands to reason that one of the ways that you can make your content more “helpful” is by leveraging this concept in your own content. Where can you add perspectives that haven’t been written about? Is there unique data that you can pull? Do you have custom images and screenshots that no other result in the SERP has?
A site that does this really well is Serious Eats. In their “Best Cast Iron Skillet” article, they heated up all of their products and collected custom data around the temperature at the edges and the middle of the skillet. They then graphed it all out to give them a piece of imagery that nobody else on the SERP has.
Understanding this concept can help better inform your own content strategy. When writing content don’t simply rewrite what’s already been said as it’s possible that this will get labeled as “unhelpful”. Instead, identify perspectives, assets, data and other ways to take your content that hasn’t been previously written about.
4. Prune Existing Unhelpful Content
Google’s Helpful Content Update will be a site-wide signal that evaluates if your domain has too much “unhelpful” content for users. If so, that could mean that even the organic visibility of your actually useful articles suffers. It stands to reason that one of the most effective ways that you can prepare for this update is to start removing any content that would fall into this classification.
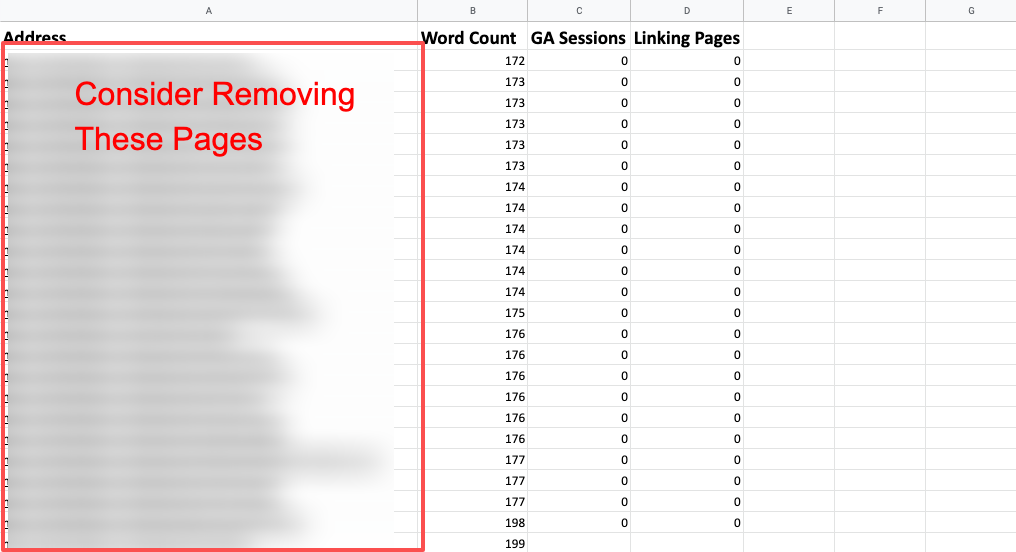
Here’s one method that you can help you start to identify thin or unhelpful content
- Open up Screaming Frog
- Connect to the Google Analytics API and the backlink API of your choice (Moz/Ahrefs). This is in Configuration > API Access
- Crawl your site using Spider mode. If needed, filter by a specific directory
- When the crawl is complete go to Internal > All and export the data
- Clean up your sheet. Remove images/JS/CSS and only keep the columns of “Address”, “Word Count” and your traffic and backlink data
- Sort in ascending order by “Word Count”
- Now you can review this list to find URLs that meet the following criteria:
- Low word count
- Low traffic
- Low link metrics
- Low revenue
- Manually inspect these pages and determine if you would consider them helpful to end users. If not, remove the page from your site.
Now there are a couple of considerations for this process:
- Just because there’s a low word count, doesn’t mean the content isn’t helpful. However, it does make it more likely.
- If possible, un-publish content instead of deleting. That way, you can always restore it later if you want.
- Also look for content that doesn’t appear to be topically relevant.
Content pruning is a way that SEOs have long used to get rid of irrelevant articles on their sites to improving rankings. We’ve seen success when using this strategy for clients in the past. This can be an excellent way of putting your site in a good position to have a greater number of articles evaluated as “helpful”.
5. Add Trust Signals To Product Review Content
Another ongoing battle between Google and creators has been in the domain of affiliate sites. Typically, these are websites that use product reviews as a content strategy. A creator writes a review (The Best Coffee Makers Of 2022) that lists different products under a certain category. The creator then earns a commission based on the amount of sales that article refers to a third party site such as Amazon. Traditionally the model for affiliate sites has been for the creator to write content around a niche, optimize for “best” keywords and try to generate organic traffic to these third party retailers.
Put simply, Google still doesn’t trust affiliate sites.
Affiliate sites are inherently incentivized by the commissions they earn off traffic referrals. This means that the products they “recommend” are much more likely to have a high AOV in order the maximize their earnings. As well, since this is a passive income strategy, it’s questionable how many authors have any real expertise in the area or actually even handled the products physically.
Once again, this puts Google’s search product at risk. There’s certainly huge potential for the search engine to rank sites whether the author is giving advice on which product to review but has never used any of the products themselves. Instead, they simply repurpose content that’s already been written. Maybe they even make their content more comprehensive but don’t add anything new to the conversation.
In the past few years, we’ve seen Google implement multiple “Product Review” updates in April 2021 & July 2022. They’ve even provided extensive guidance on how websites can put themselves in a good position during these updates. These mainly involve recommendations to showcase to Google that you’ve actually used the product by using custom assets, using product data and describing the pros/cons of specific products.
The “Helpful Content Update” might be a continuation of Google’s crackdown on affiliate sites. Google even directly references this in one of their questions “Are you keeping in mind our guidance for core updates and for product reviews?“. Affiliate sites are notorious at repurposing information that already exists and may be at higher risk during this update.
Search News Straight To Your Inbox
*Required
Join thousands of marketers to get the best search news in under 5 minutes. Get resources, tips and more with The Splash newsletter: