One of the biggest changes in SEO this year has been the evolution of search results; rich snippets, structured snippets, & direct answers. We’ve been keeping an eye on how Google and Bing are keeping up with each other in making changes to their search results. Google has the knowledge panel next to search results to show off information about different entities, and Bing shows what they call SnapShots in that area.
Related Content:
I wanted to find out more about how Bing worked with their knowledge panels to see what it was like compared to Google’s knowledge graph. I know that Microsoft’s knowledge panel is referred to as Satori. According to the Bing Blog, Satori is Japanese for “Understanding”. The blog post tells us:
Over time, Satori will continue growing to encompass billions of entities and relationships, providing searchers with a more useful model of the digital and physical world.
That seemed like a good start, so I searched the USPTO (United States Patent and Trademark Office) database to try to find any patents from Microsoft that referred to the name, and I found one. Satori is referred to in one Microsoft patent as an “entity store” where information about entities is kept. That patent tells us:
In semantic web terminology, an entity is a set of structured attributes that uniquely identifies a person. Attributes of a typical person entity include name, user identification (id), date of birth, place of birth, occupation, and the source Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that was used to identify the entity. The current methods used to identify authoritative images of a person entity have many drawbacks.
One approach utilizes face recognition technologies, manually identifies the first image, and uses that image to recognize other images for the person entity. Unfortunately, this approach requires the image to be frontal and non-rotated. Many images do not meet these requirements. This approach is also difficult to scale because of the number of people and images in a search engine index.
Another approach utilizes a traditional search engine ranking. Structure data associated with the entity is utilized to augment the query and retrieve images within documents that have keywords contained in the augmented query. However, this approach suffers from several issues. The document may contain multiple images and it is difficult to identify which image belongs to the person entity. Multiple people entities with the same name may cause the image to be associated with the wrong entity. In some instances, the name of the person entity is similar to the name of a non-person entity which may cause the non-person image to be associated with the person entity.
So this patent targets associating people with images that “uniquely identify them”.
It makes me feel good that when I search for my name at Bing, that a snapshot side panel search result is returned with an image of me that I’ve used in several profiles for myself on the Web:

This is what appears in the Bing SnapShot on a search for my name – an associated image of me
The patent that mentions Microsoft’s Satori tells us that it follows a process to learn to associate images with the different entity:
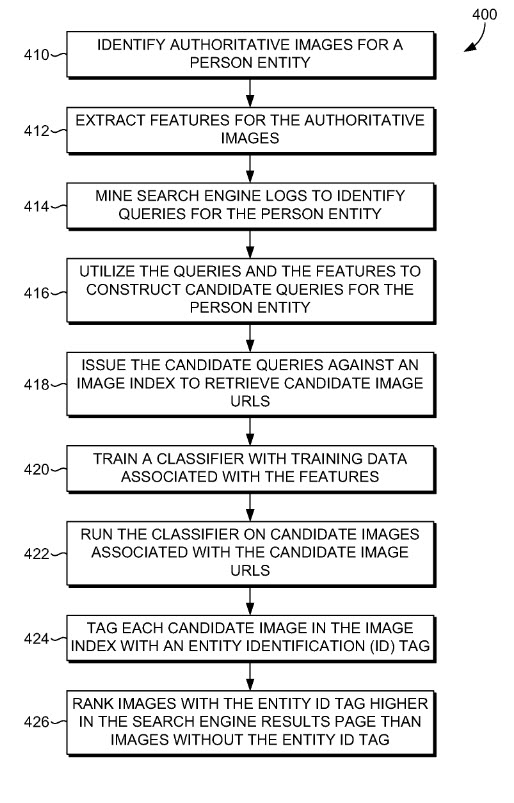
Features are extracted for authoritative images. Search engine logs are mined to identify queries for the person entity. The queries and features are utilized to construct candidate queries for the person entity. The candidate queries are issues against a search engine image index to retrieve candidate image uniform resource locators (URLs). A classifier is trained with training data associated with the features and run on candidate images associated with the candidate image URLs. Each candidate image is tagged with an entity identification (ID) tag. The images with the entity ID tag are ranked higher in the search engine results page than images without the entity ID tag.
The patent is:
Discovering Authoritative Images of People Entities
Invented by Ayman Malek Abdel Hamid Kaheel, Padma Priya Gaggara, Prakash Asirvatham Arul, Mohammad Adil Hafeez, Dhananjay Dilip Kulkarni, and Kancheng Cao
Assigned to Microsoft
US Patent Application 20140177966
Published June 26, 2014
Filed: December 20, 2012
Abstract
Systems, methods, and computer storage media for discovering authoritative images of people entities are provided. Selections of person entities are received. Authoritative URLs and authoritative images for the person entities are identified. Once the authoritative images are identified, features are extracted. Queries for the person entities are identified by mining search engine logs. The queries and features can be utilized to construct candidate queries to identify and retrieve candidate image URLs. Candidate features are extracted for each candidate image associated with the candidate image URLs. Training data may be utilized to train a classifier that can be run on each candidate image. Each candidate image can then be tagged with an entity ID tag. Images with the entity ID tag can be ranked higher in search engine results page than images without the entity ID tag.
A “person entity,” is a set of structured features that uniquely identifies a person. The features of a typical person entity can include:
- name
- user identification (ID)
- date of birth
- place of birth
- occupation, and
- the source Uniform Resource Locator (URL) that was used to identify the entity
Other features may be identified and extracted for authoritative images of people entities. It involves:
- Extracting similar entities to the person entity
- identifying authoritative uniform resource locators (URLs) for the person entity
- Identifying authoritative images for the person entity; and
- Extracting features for the authoritative images
A computing Device may follow these steps involving a person entity. The method includes:
- Identifying authoritative images for a person entity
- Extracting features for the authoritative images
- Mining search engine logs to identify queries for the person entity
- Utilizing the queries and the features to construct candidate queries for the person entity
- Issuing the candidate queries against a search engine image index to retrieve candidate image URLs
- Training a classifier with training data associated with the features
- Running the classifier on candidate images associated with the candidate image URLs
- Tagging each candidate image with an entity identification (ID) tag; and
- Ranking images with the entity ID tag higher in the search engine results page than images without the entity ID tag
Here’s a flow chart from the patent’s drawings that illustrates a number of these steps:
The entity store for a person (e.g., Satori) contains structured attributes of people entities, that can be used to “help resolve situations where one person shares a name with a nonperson entity.”
The patent provides more details on how authoritativeness might be figured for an entity, and how images are associated with queries. In learning more about Google Knowledge panel results, I looked at the patent I wrote about in the blog post How Google Decides What to Know in Knowledge Graph Results This patent from Microsoft doesn’t tell us a lot more about what’s contained in Bing’s Snap shots, but it does give us something to compare.
Has Bing Associated an Authoritative image with you?
Search News Straight To Your Inbox
*Required
Join thousands of marketers to get the best search news in under 5 minutes. Get resources, tips and more with The Splash newsletter: