Table of Contents
The Clustering Entities Patent Is Updated
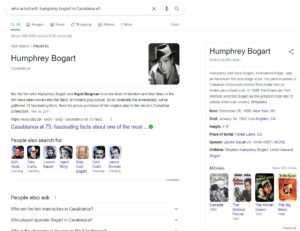
One of my latest blog posts was about Google clustering news results by topic in organic search results. Google has clustered information about entities in search results as well. If you now search for people who acted with Humprey Bogart in Casablanca. You can see other actors in that movie in those search results. You can also see related questions that include those actors and the film (and that ontology about associated categories for the movie). This new post is about entity clustering and a change to how Google is delivering search results related to entity clustering.
Related Content:
- Technical SEO Agency
- Ecommerce SEO Agency
- Shopify SEO Services
- Franchise SEO Agency
- Enterprise SEO Services
Here is an example of search results that show connections between actors and the movie Casablanca:
Google has a continuation patent from January 3, 2022. I had written about an earlier version of that patent in 2019 in the post Entity Clustering in Google Search Results
Claims From the First Patent
Since this new patent is a continuation patent, most of the patent is identical. The patent contains updated claims. The first claim from the 2019 version of the Clustering Search Results patent reads as follows:
1. A method comprising: determining items responsive to a query; generating first-level clusters of the items, each cluster representing an entity in a knowledge base and including items mapped to the entity; calculating a respective cluster score for each first-level cluster, wherein the respective cluster score for a first-level cluster is based on a respective silhouette score that measures coherence and separation of the first-level cluster and on a silhouette ratio representing a percentage of all first-level clusters having a respective silhouette score above a threshold; merging the first-level clusters based on entity ontology relationships and on respective cluster scores calculated for the merged clusters, wherein the respective cluster score of a merged cluster represents a better score than the respective cluster scores for first-level clusters included in the merged cluster; applying hierarchical clustering to the merged clusters, producing final clusters that maximize respective cluster scores for the hierarchical clustering; and providing the items responsive to the query for display according to the final clusters.
Claims From the Updated Patent
In detail, the post I wrote in 2019 describes the process behind the clustering entities patent. Now, the new version of the patent from the first day of 2022 has a new language that tells us what the patent does. The first set of claims in 1999 told us about a “silhouette score,” which is not in the new claims. The 2022 claims include some terms that aren’t in the 2019 version:
1. A method performed by a search engine comprising: determining a set of items responsive to a query; for each item of the set of items determined to be responsive to the query: identifying one or more entities associated with the item, and obtaining an embedding for the item; generating first-level clusters from the set of items, each cluster representing an entity of the one or more entities; producing final clusters by merging the first-level clusters based on entity ontological relationships and embedding similarities determined using the item embeddings, wherein the entity ontological relationships include hypernym, synonym, and co-hypernym; and providing items from the set of items responsive to the query for display according to the final clusters.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein first-level clusters that are smaller are merged first.
3. The method of claim 2, wherein merging the first-level clusters that are smaller includes, for a first first-level cluster: determining a second first-level cluster and a third first-level cluster related to the first first-level cluster based on the entity ontological relationships; determining that the third first-level cluster and the first first-level cluster are smaller than the second first-level cluster; and merging the first first-level cluster with the third first-level cluster.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein first-level clusters that are most similar are merged first.
5. The method of claim 4, wherein merging first clusters that are most similar first includes, for a first first-level cluster: determining a second first-level cluster and a third first-level cluster related to the first first-level cluster in the entity ontological relationships; determining that the first first-level cluster is more similar to the second first-level cluster than the third first-level cluster; and merging the first first-level cluster with the second first-level cluster.
The newer version tells us it includes “ontological relationships,” which the first set of claims doesn’t. So, we know from the SERPs that Bogart was in the Movie “Casablanca,” as were many other actors who were focused on that search result.
Clustering search results
Inventors: Jilin Chen, Dai; Lichan Hong, Tianjiao Zhang, Huazhong Ning, and Ed Huai-Hsin Chi
Assignee: Google LLC
US Patent: 11,216,503
Granted: January 4, 2022
Filed: November 26, 2019
Abstract
Implementations provide an improved system for presenting search results based on entity associations of the search items. An example method includes generating first-level clusters of items responsive to a query, each cluster representing an entity in a knowledge base and including items mapped to the entity, merging the first-level clusters based on entity ontology relationships, applying hierarchical clustering to the merged clusters, producing final clusters, and initiating display of the items according to the final clusters. Another example method includes generating first-level clusters from items responsive to a query, each cluster representing an entity in a knowledge base and including items mapped to the entity, producing final clusters by merging the first-level clusters based on an entity ontology and an embedding space that is generated from an embedding model that uses the mapping, and initiating display of the items responsive to the query according to the final clusters.
If you travel back to my original writeup of this clustering entities patent from 2019, you will see that I mention “ontologies” many times when writing about entities. The 2022 version of the clustering entities patent adds that language directly to the claims. They are in the SERPs without discussing the relationship between the movie and its actors.
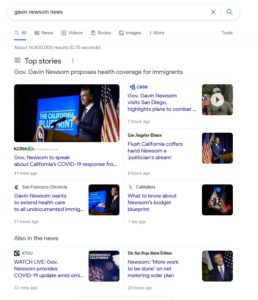
Clustering Entities and News
After this change, when we search for a specific entity and news, we also see clustered search results there as well:
So Google is no longer sorting SERPs based on how good a match documents are for query terms – Google is clustering topics and relationships between entities as part of its decision on what to include in search results.
Search News Straight To Your Inbox
*Required
Join thousands of marketers to get the best search news in under 5 minutes. Get resources, tips and more with The Splash newsletter: